前言
最近項目中使用到了Mybatis持久層框架哩簿,由于從來沒有深入的了解過基于Java語言實現(xiàn)的持久層框架宵蕉,于是有點心血來潮,所以就有了這篇長文节榜。下面是來自mybatis官網(wǎng)對其的簡單介紹羡玛。
MyBatis 是支持定制化 SQL、存儲過程以及高級映射的優(yōu)秀的持久層框架宗苍。MyBatis 避免了幾乎所有的 JDBC 代碼和手動設(shè)置參數(shù)以及獲取結(jié)果集稼稿。MyBatis 可以對配置和原生Map使用簡單的 XML 或注解,將接口和 Java 的 POJOs(Plain Old Java Objects,普通的 Java對象)映射成數(shù)據(jù)庫中的記錄讳窟。
深入方式
個人覺得最好的學習新東西的方式就是demo让歼,所以打算從頭到位搭建一個demo來貫通整篇文章,下面一一介紹demo中用到的文件挪钓,完整示例可參考附件是越。
Demo入口 (MybatisDemo.java)
import com.hackx.hackspring.domain.memeber.MemberDO;
import com.hackx.hackspring.mapper.member.MemberMapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Created by hackx on 9/26/16.
*/
public class MybatisDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-demo-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
MemberMapper memberMapper = session.getMapper(MemberMapper.class);
MemberDO memberDO = memberMapper.queryById(1L);
System.out.println(memberDO.toString());
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
}
Mybatis配置 (mybatis-demo-config.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.hackx.hackspring.domain"/>
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_spring"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="admin"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mappers/member-mapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
Mapper XML (member-mapper.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.hackx.hackspring.mapper.member.MemberMapper">
<resultMap id="MemberDOResult" type="MemberDO">
<result property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="gmtCreate" column="gmt_create"/>
<result property="gmtModified" column="gmt_modified"/>
<result property="name" column="name"/>
<result property="age" column="age"/>
<result property="email" column="email"/>
<result property="password" column="password"/>
</resultMap>
<sql id="MemberDOFields">
id, gmt_create, gmt_modified, name, age, email, password
</sql>
<!-- id必須與Mapper中對應(yīng)的方法的名稱一致 -->
<select id="queryById" resultMap="MemberDOResult" parameterType="java.lang.Long">
SELECT
<include refid="MemberDOFields"/>
FROM members
WHERE id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
Mapper 接口(MemberMapper.java)
import com.hackx.hackspring.domain.memeber.MemberDO;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* Created by hackx on 8/21/16.
*/
@Mapper
public interface MemberMapper {
MemberDO queryById(Long id);
}
DataObject (MemberDO.java)
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Created by hackx on 8/21/16.
*/
public class MemberDO implements Serializable {
/**
* 主鍵ID
*/
private Long id;
/**
* 創(chuàng)建時間
*/
private Date gmtCreate;
/**
* 修改時間
*/
private Date gmtModified;
/**
* 會員名稱
*/
private String name;
/**
* 會員年齡
*/
private Integer age;
/**
* 會員郵箱地址
*/
private String email;
/**
* 會員密碼
*/
private String password;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Date getGmtCreate() {
return gmtCreate;
}
public void setGmtCreate(Date gmtCreate) {
this.gmtCreate = gmtCreate;
}
public Date getGmtModified() {
return gmtModified;
}
public void setGmtModified(Date gmtModified) {
this.gmtModified = gmtModified;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MemberDO{" +
"id=" + id +
", gmtCreate=" + gmtCreate +
", gmtModified=" + gmtModified +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", email='" + email + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
上述就是此Demo用到的所有相關(guān)的文件耳舅,下面按照程序運行的順序依次介紹Mybatis的核心功能模塊碌上。
Mybatis應(yīng)用入口之配置文件
每個基于 MyBatis 的應(yīng)用都是以一個 SqlSessionFactory 的實例為中心的倚评。SqlSessionFactory 的實例可以通過 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 獲得。而 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 則可以從 XML 配置文件或一個預先定制的 Configuration 的實例構(gòu)建出 SqlSessionFactory 的實例馏予。所以Mybatis的入口點加載Mybatis的配置文件(本示例中的mybatis-demo-config.xml), Mybatis源碼中org.apache.ibatis.io包下負責文件的讀取天梧,將本地文件以Reader(字符)或者InputStream(字節(jié))的方式讀入內(nèi)存. 下面兩行代碼完成了Mybatis配置文件的加載過程。
String resource = "mybatis-demo-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
加載過程中霞丧,主要涉及了兩個類:Resources和ClassLoaderWrapper,兩個類都在包org.apache.ibatis.io下呢岗。下面我們先簡單介紹下Resources類:
Resources類
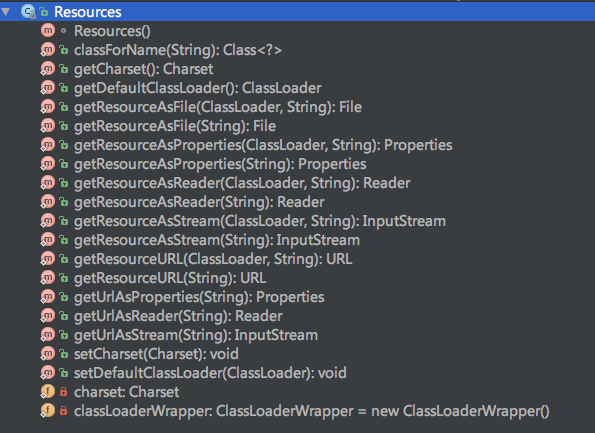
上圖是Resources類中含有的成員變量和方法的簽名,其中有幾個比較重要的方法:
public static URL getResourceURL(ClassLoader, String)
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(ClassLoader, String)
public static Properties getResourceAsProperties(ClassLoader, String)
public static Reader getResourceAsReader(ClassLoader, String)
public static File getResourceAsFile(ClassLoader, String)
以上幾個不同的方法提供了文件在內(nèi)存的不同表現(xiàn)形式蛹尝,相信每個方法的意義后豫,我們從字面上就已經(jīng)很好的理解了。對于加載Mybatis配置XML文件而言突那,最常用的是下面兩個方法:
public static InputStream getResourceAsStream(ClassLoader, String)
public static Reader getResourceAsReader(ClassLoader, String)
ClassLoaderWrapper類
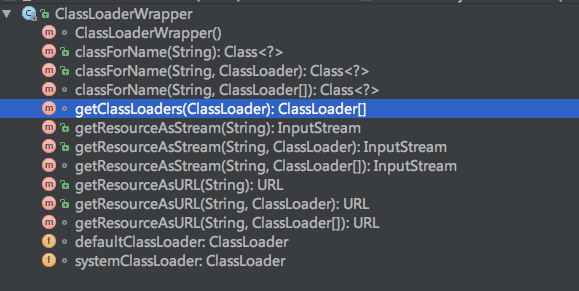
Resources類在Mybatis配置文件加載的過程中挫酿,僅僅是為Mybatis框架提供接口,并不參與真正的文件加載操作愕难。而真正的文件加載到內(nèi)容的操作是由ClassLoaderWrapper完成的早龟。ClassLoaderWrapper封裝了java.lang.ClassLoader這個類,而配置文件的加載是使用ClassLoader完成的猫缭。下圖是配置文件加載的時序圖葱弟。
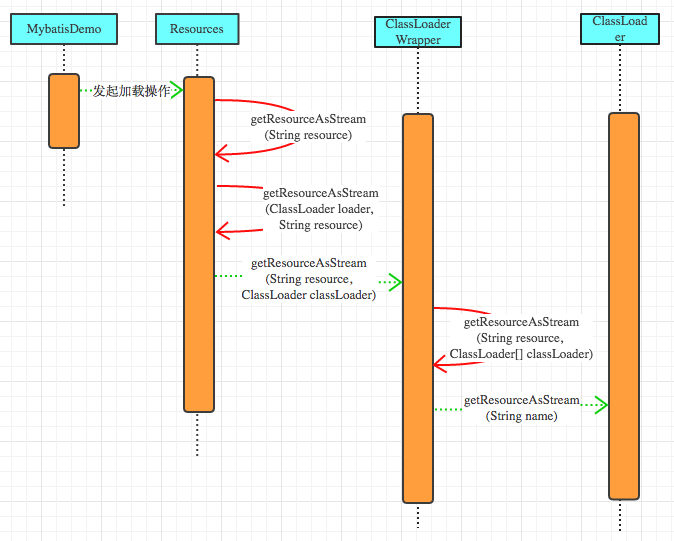
ClassLoader是java提供對外開放的類加載機制,至于ClassLoader的詳細使用猜丹,可以參考這兩篇文章深入分析Java ClassLoader原理 , Java Classloader Wiki 詳細了解下芝加,本文不再做過多的介紹。
SqlSessionFactory創(chuàng)建
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder根據(jù)Resources類生成返回的配置文件inputStream來構(gòu)建SqlSessionFactory射窒,一旦創(chuàng)建了SqlSessionFactory,就不再需要它了妖混,其中涉及到的相關(guān)類的關(guān)系如下:
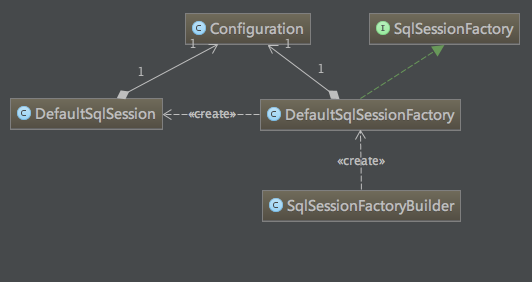
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder實例調(diào)用build方法,返回SqlSessionFactory實例
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
而真正執(zhí)行build邏輯的是下面通的用build方法轮洋,注意這里的environment和properties均為null
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
從上述代碼中我們可以看出制市,首先創(chuàng)建了XMLConfigBuilder實例,暫時先忽略XMLConfigBuilder的執(zhí)行邏輯弊予,后面會詳細介紹祥楣;然后調(diào)用XMLConfigBuilder實例的parse方法,返回一個Configuration對象汉柒,然后將返回的Configuration對象當作參數(shù)傳給下面的build方法误褪,生成SqlSessionFactory實例。
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
在SqlSessionFactory創(chuàng)建過程中碾褂,我們用到了XMLConfigBuilder兽间,它與Configuration類的關(guān)系如下圖,
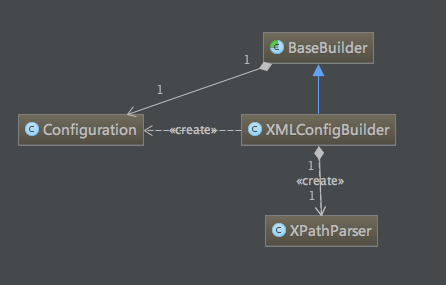
XMLConfigBuilder構(gòu)造方法
//創(chuàng)建XPathParser實例
public XMLConfigBuilder(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties props) {
this(new XPathParser(inputStream, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
}
其中比較重要的部分是創(chuàng)建XPathParser實例
//創(chuàng)建XPathParser實例
public XPathParser(InputStream inputStream, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
commonConstructor(validation, variables, entityResolver);
this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(inputStream));
}
commonConstructor完成的工作如下,最重要的是創(chuàng)建了了xpath實例對象正塌,有了它嘀略,我們有可以使用JDK提供的Xpath工具類來來解析XML文件了(此處為mybatis-demo-config.xml)
private void commonConstructor(boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) {
this.validation = validation;
this.entityResolver = entityResolver;
this.variables = variables;
XPathFactory factory = XPathFactory.newInstance();
this.xpath = factory.newXPath();
}
構(gòu)建了XMLConfigBuilder的實例后恤溶,調(diào)用其parse()方法,其中parser.evalNode("/configuration")獲取到的是根結(jié)點
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
然后通過以parser.evalNode("/configuration")返回的根節(jié)點為參數(shù)帜羊,調(diào)用parseConfiguration咒程,分別將對應(yīng)的值解析出來塞進
Configuration實例configuration中
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
Properties settings = settingsAsPropertiess(root.evalNode("settings"));
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectionFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectionFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
從parseConfiguration中我們可以看出mybatis配置文件的大致結(jié)構(gòu),根節(jié)點為configuration讼育,子節(jié)點包括properties帐姻、typeAliases、plugins奶段、objectFactory饥瓷、objectWrapperFactory、reflectionFactory痹籍、environments扛伍、databaseIdProvider、typeHandlers词裤、mappers刺洒、settings等,因為我們平時大部分都是使用Spring來進行管理的吼砂,所有有些配置項可能會比較陌生逆航,隨后我們會重點解釋。上述代碼中比較重要的類有XNode,XPathParser渔肩;XNode是Node類的擴展,XPathParser是xml文件的解析器工具類因俐。XPathParser中比較重要的方法是:public XNode evalNode(String expression)而evalNode最終調(diào)用的是com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.jaxp.XPathImpl
里的public Object evaluate(String expression, Object item, QName returnType).
下面是解析mappers的源碼,供參考周偎。
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
SqlSession創(chuàng)建
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
通過調(diào)用sqlSessionFactory的openSession方法來創(chuàng)建SqlSession實例
//DefaultSqlSessionFactory里的openSession
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
上述代碼涉及到了執(zhí)行器抹剩,因為最終我們是要執(zhí)行SQL的,所以這東西一定不能少蓉坎。執(zhí)行器有三類:SIMPLE(普通執(zhí)行器),REUSE(執(zhí)行器會重用預處理語句)和BATCH(執(zhí)行器將重用語句并批量執(zhí)行)
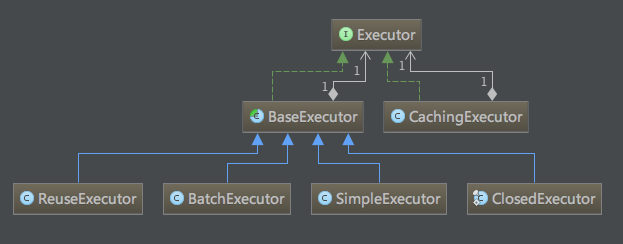
//執(zhí)行器生成過程
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
在生成執(zhí)行器時有個是否緩存的判斷if (cacheEnabled),這個配置時二級緩存的開關(guān)澳眷,在配置mybatis的時候,可按照下面的配置將二級緩存打開
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
執(zhí)行器創(chuàng)建后,通過生成DefaultSqlSession的實例對象蛉艾,最終創(chuàng)建SqlSession钳踊,需要注意的是SqlSession 實例不是線程安全的,是不能被共享的,所以它的最佳范圍是請求或方法范圍.每個線程都應(yīng)該有自己的SqlSession實例.
public DefaultSqlSession(Configuration configuration, Executor executor, boolean autoCommit) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.executor = executor;
this.dirty = false;
this.autoCommit = autoCommit;
}
Member對象創(chuàng)建及SQL執(zhí)行
這個過程沒看太懂,其中涉及了一些Proxy代理的東西勿侯,先把代碼羅列在這拓瞪,后續(xù)在慢慢補充。
MemberMapper memberMapper = session.getMapper(MemberMapper.class);
MemberDO memberDO = memberMapper.queryById(1L);
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}