使用最為基本的用法:
Glide.with(this).load(imageUr).into(imageView);
Glide.with(this)
分析
0凑懂、先來看看RequestManager中的成員變量
public class RequestManager implements LifecycleListener {
private final Context context;
/**生命周期管理**/
private final Lifecycle lifecycle;
private final RequestManagerTreeNode treeNode;
private final RequestTracker requestTracker;
private final Glide glide;
/**配置注入者**/
private final OptionsApplier optionsApplier;
/**默認(rèn)的配置**/
private DefaultOptions options;
}
1或详、RequestManagerRetriever.get()獲取到RequestManagerRetriever的單例乒躺;
2、retriever.get(activity)獲取到RequestManager的實(shí)例,作用是:
這里會根據(jù)當(dāng)前代碼的所處線程和activity的類別(Activity,F(xiàn)ragmentActivity,F(xiàn)rament和context(contextWrapper))善绎,getApplicationManager到不同的RequestManager。
-如果是后臺線程诫尽,會再次詢問是否仍在后臺線程中運(yùn)行禀酱,如果是的話就創(chuàng)建一個(gè)RequestManager的對象
private RequestManager getApplicationManager(Context context) {
// Either an application context or we're on a background thread.
if (applicationManager == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (applicationManager == null) {
// Normally pause/resume is taken care of by the fragment we add to the fragment or activity.
// However, in this case since the manager attached to the application will not receive lifecycle
// events, we must force the manager to start resumed using ApplicationLifecycle.
applicationManager = new RequestManager(context.getApplicationContext(),
new ApplicationLifecycle(), new EmptyRequestManagerTreeNode());
}
}
}
return applicationManager;
}
從注釋中可以得知:處于后臺運(yùn)行中的或者使用Application創(chuàng)建的RequestManager,是不能監(jiān)聽到Application已經(jīng)啟動的回調(diào)的,于是就force the manager to start resumed using ApplicationLifecycle牧嫉。
-如果在非后臺線程:
-FragmentActivity:
public RequestManager get(FragmentActivity activity) {
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
return get(activity.getApplicationContext());
} else {
assertNotDestroyed(activity);
/**每次都會新建一個(gè)FragmentManager的對象**/
FragmentManager fm = activity.getSupportFragmentManager();
return supportFragmentGet(activity, fm);
}
}
.load(imageUrl)
/**
* Returns a request builder to load the given {@link java.lang.String}.
* signature.
*
* @see #fromString()
* @see #load(Object)
*
* @param string A file path, or a uri or url handled by {@link com.bumptech.glide.load.model.UriLoader}.
*/
public DrawableTypeRequest load(String string) {
return (DrawableTypeRequest) fromString().load(string);
}
fromString()
private DrawableTypeRequest loadGeneric(Class modelClass) {
ModelLoader streamModelLoader = Glide.buildStreamModelLoader(modelClass, context);
ModelLoader fileDescriptorModelLoader =
Glide.buildFileDescriptorModelLoader(modelClass, context);
if (modelClass != null && streamModelLoader == null && fileDescriptorModelLoader == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown type " + modelClass + ". You must provide a Model of a type for"
+ " which there is a registered ModelLoader, if you are using a custom model, you must first call"
+ " Glide#register with a ModelLoaderFactory for your custom model class");
}
/**利用配置注入者將配置注入**/
return optionsApplier.apply(
new DrawableTypeRequest(modelClass, streamModelLoader, fileDescriptorModelLoader, context,
glide, requestTracker, lifecycle, optionsApplier));
}
這樣剂跟,就得到了一個(gè)DrawableTypeRequest(繼承與GenericRequestBuilder),以下是繼承關(guān)系圖(as中按F4)
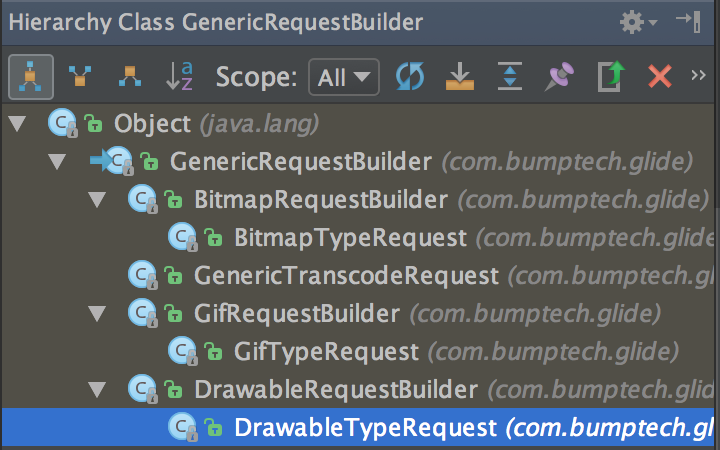
load()
這個(gè)倒是沒有什么酣藻,就是說明接下來使用的DrawableTypeRequest中的ModelType是何種類型的曹洽。而這個(gè)ModelType解釋是:
The type of model representing the resource.
into()
return into(glide.buildImageViewTarget(view, transcodeClass));
會先生成一個(gè)ImageViewTarget
public class ImageViewTargetFactory {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Target buildTarget(ImageView view, Class clazz) {
if (GlideDrawable.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return (Target) new GlideDrawableImageViewTarget(view);
} else if (Bitmap.class.equals(clazz)) {
return (Target) new BitmapImageViewTarget(view);
} else if (Drawable.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return (Target) new DrawableImageViewTarget(view);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unhandled class: " + clazz
+ ", try .as*(Class).transcode(ResourceTranscoder)");
}
}
}
再來執(zhí)行最終的生成request對象和request的過程
/**
* Set the target the resource will be loaded into.
*
* @see Glide#clear(com.bumptech.glide.request.target.Target)
*
* @param target The target to load the resource into.
* @return The given target.
*/
public > Y into(Y target) {
Util.assertMainThread();
if (target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must pass in a non null Target");
}
if (!isModelSet) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("You must first set a model (try #load())");
}
/**其實(shí)就是獲取view中的tag(Request對象)**/
Request previous = target.getRequest();
/**如果該view有已經(jīng)有Request請求了,那么就先取消**/
if (previous != null) {
previous.clear();
requestTracker.removeRequest(previous);
previous.recycle();
}
Request request = buildRequest(target);
/**設(shè)置view的tag **/
target.setRequest(request);
/**添加請求過程中的生命周期**/
lifecycle.addListener(target);
requestTracker.runRequest(request);
return target;
}
然后就runRequest了
/**
* Starts tracking the given request.
*/
public void runRequest(Request request) {
requests.add(request);
if (!isPaused) {
request.begin();
} else {
pendingRequests.add(request);
}
}
接下來就是request開始執(zhí)行:
先來看看Engine都有什么成員變量
public class Engine implements EngineJobListener,
MemoryCache.ResourceRemovedListener,
EngineResource.ResourceListener {
private static final String TAG = "Engine";
/**存儲EngineJob的集合**/
private final Map jobs;
private final EngineKeyFactory keyFactory;
private final MemoryCache cache;
private final EngineJobFactory engineJobFactory;
private final Map>> activeResources;
private final ResourceRecycler resourceRecycler;
private final LazyDiskCacheProvider diskCacheProvider;
// Lazily instantiate to avoid exceptions if Glide is initialized on a background thread. See #295.
private ReferenceQueue> resourceReferenceQueue;
/**
* Allows a request to indicate it no longer is interested in a given load.
*/
public static class LoadStatus {
private final EngineJob engineJob;
private final ResourceCallback cb;
public LoadStatus(ResourceCallback cb, EngineJob engineJob) {
this.cb = cb;
this.engineJob = engineJob;
}
public void cancel() {
engineJob.removeCallback(cb);
}
}
EngineRunnable****(實(shí)際進(jìn)行圖片請求的****task)
@Override
public void run() {
......
Exception exception = null;
Resource resource = null;
try {
/** task運(yùn)行的核心代碼**/
resource = decode();
} catch (Exception e) {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Exception decoding", e);
}
exception = e;
}
......
}
然后會執(zhí)行decode()方法
private Resource decode() throws Exception {
if (isDecodingFromCache()) {
return decodeFromCache();
} else {
return decodeFromSource();
}
}
看decodeResultFromCache()方法
public Resource decodeResultFromCache() throws Exception {
if (!diskCacheStrategy.cacheResult()) {
return null;
}
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
Resource transformed = loadFromCache(resultKey);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Decoded transformed from cache", startTime);
}
startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
/**這里把從cache中拿到的結(jié)果進(jìn)行轉(zhuǎn)碼,后面做詳細(xì)的分析**/
Resource result = transcode(transformed);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Transcoded transformed from cache", startTime);
}
return result;
}
private Resource decodeSource() throws Exception {
Resource decoded = null;
try {
long startTime = LogTime.getLogTime();
/**使用ExecutorService組織請求**/
final A data = fetcher.loadData(priority);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Fetched data", startTime);
}
if (isCancelled) {
return null;
}
decoded = decodeFromSourceData(data);
} finally {
fetcher.cleanup();
}
return decoded;
}
其中fetcher是接口DataFetcher對象辽剧,DataFetcher的實(shí)現(xiàn)類包括:
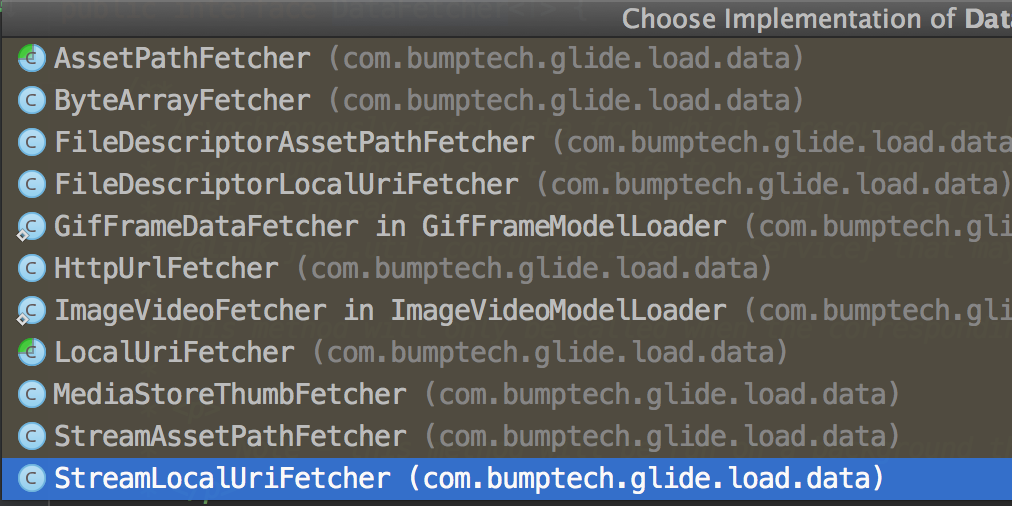
以
HttpUrlFetcher為例分析:
@Override
public InputStream loadData(Priority priority) throws Exception {
return loadDataWithRedirects(glideUrl.toURL(), 0 /*redirects*/, null /*lastUrl*/, glideUrl.getHeaders());
}
-glideUrl.toURL():這里需要安全的裝換到一個(gè)可以訪問的URL,具體可見http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3286067/url-encoding-in-android
final int statusCode = urlConnection.getResponseCode();
if (statusCode / 100 == 2) {
return getStreamForSuccessfulRequest(urlConnection);
} else if (statusCode / 100 == 3) {
String redirectUrlString = urlConnection.getHeaderField("Location");
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(redirectUrlString)) {
throw new IOException("Received empty or null redirect url");
}
URL redirectUrl = new URL(url, redirectUrlString);
return loadDataWithRedirects(redirectUrl, redirects + 1, url, headers);
} else {
if (statusCode == -1) {
throw new IOException("Unable to retrieve response code from HttpUrlConnection.");
}
throw new IOException("Request failed " + statusCode + ": " + urlConnection.getResponseMessage());
}
-如果返回的code是3開頭的重定向請求送淆,那么需要獲取重定向的地址,重新組織訪問怕轿。