大家都知道OC是動態(tài)語言又固,其主要特征就是動態(tài)綁定仲器,消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)。我們在調(diào)用NS方法的時候仰冠,runtime其實就已經(jīng)在背后默默為我們干活了乏冀。還記得剛開始學(xué)習(xí)iOS時,我一聽到發(fā)送消息就自然而然的聯(lián)想到---調(diào)用方法洋只,這實在是太委屈強大的OC了辆沦。或許很多人會有和我一樣的看法识虚,別急肢扯,看完本篇文章之后,你的看法就會發(fā)生改變了担锤。
本文嘗試講解OC中類蔚晨,對象等在runtime中的結(jié)構(gòu),還有動態(tài)綁定肛循,發(fā)送消息铭腕,消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)银择,動態(tài)添加方法,調(diào)換方法等幾個方面講解runtime的基礎(chǔ)知識谨履,后面會用一個demo告訴大家具體的使用方法。
runtime的源碼是開源的熬丧,附上傳送門Objective-C Runtime源碼笋粟。
OC的動態(tài)特性
OC拓展了C語言,加入了smallTalk的消息傳遞和面向?qū)ο蟮奶攸c析蝴,它是一個動態(tài)語言害捕,這個動態(tài)體現(xiàn)在三個方面。
動態(tài)類型
例如id類型的實例闷畸,其類型需要等到運行時才能決定尝盼,在編譯時id就是一個通用類型,通常我們會這么干
id anIns;
if ([anIns isKindOfClass:[SomeClass class]]) {
SomeClass *sClass = (SomeClass *)anIns;
//do something after introspection
}
動態(tài)綁定
基于動態(tài)類型,實例所屬的類在運行時才確定佑菩,動態(tài)綁定就是在這個實例類型確定后將具體的屬性和方法綁定到這個實例上盾沫,這些屬性和方法包括沒有在類上實現(xiàn)的,所以利用這個特性殿漠,我們可以動態(tài)的添加屬性和方法赴精。
在標(biāo)準(zhǔn)的C語言中:
#improt <studio.h>
void printHello() {
printf("Hello, World!\n");
}
void printBye() {
printf("GoodBye, World!\n");
}
void doIt(int type) {
if (type == 0) {
printHello();
}else {
printBye();
}
}
這兩個方法的具體實現(xiàn)都是在編譯時就已經(jīng)知道了,編譯器直接調(diào)用了這個方法绞幌,這個函數(shù)的地址已經(jīng)被硬編碼蕾哟。
如果把上面的代碼改成這樣呢:
#improt <studio.h>
void printHello() {
printf("Hello, World!\n");
}
void printBye() {
printf("GoodBye, World!\n");
}
void doIt(int type) {
void (*fnc)();
if (type == 0) {
fnc = printHello;
}else {
fnc = printBye;
}
fnc();
reuturn 0;
}
修改之后,fnc的具體實現(xiàn)需要等到運行時才會知道莲蜘,與第一個例子相比谭确,調(diào)用fnc時取出fnc的地址。
動態(tài)加載
根據(jù)需求加載所需要的資源票渠,這點很容易理解逐哈,對于iOS開發(fā)來說,基本就是根據(jù)不同的機型做適配问顷。最經(jīng)典的例子就是在Retina設(shè)備上加載@2x鞠眉,@3x的圖片,而在老一些的普通屏設(shè)備上加載原圖择诈。
object械蹋、class在runtime中的結(jié)構(gòu)
object
在runtime中,object是一個結(jié)構(gòu)體羞芍,包含一個指向自己所屬的類的指針isa
struct objc_object {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
}
isa指針指向的是它的類別:Class,也就是它所屬的類哗戈。
這個Class:
typedeef objc_class *Class
它是一個指向objc_class結(jié)構(gòu)體的指針
對于id:
/// A pointer to an instance of a class.
typedef struct objc_object *id;
Class
對于Class,它在runtime中的定義是這樣的:
struct objc_class {
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
#if !__OBJC2__
Class super_class;
const char *name; //類名
long version; //版本號
long info; //信息
long instane_size; //實例變量占用內(nèi)存大小
struct objc_ivar_List_ *ivars //實例變量列表
struct objc_method_list **methodlists //方法列表
struct objc_cache *chche //方法緩存列表
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols //協(xié)議列表
#end if
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE
isa 指向所屬的Class荷科。
整個結(jié)構(gòu)的示意圖:
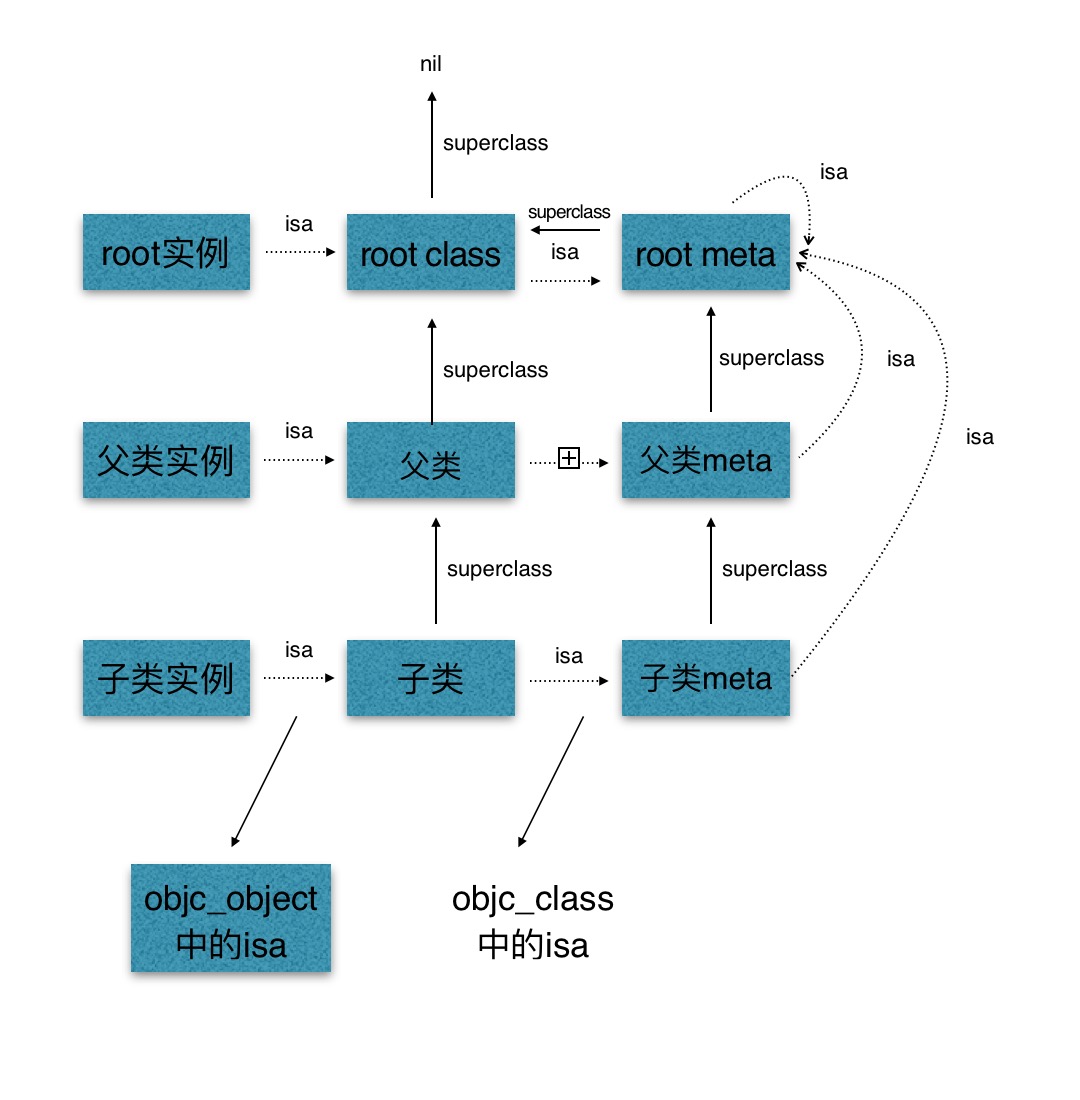
object&class
由object和class的代碼可以知道唯咬,類與對象相比只是多了實例變量和方法列表等纱注,類和對象都是對象(有點拗口),分別是類對象和實例對象胆胰。
在object中的isa指針指向的是對應(yīng)的類結(jié)構(gòu):Class狞贱,Class其中存放的是普通成員變量和實例方法(-開頭);
在class中的is指針指向的是metaClass蜀涨,metaClass中存放的是靜態(tài)成員變量和類方法(+開頭)瞎嬉。
所有的metaclass中isa指針都是指向根metaclass,而根metaclass則指向自身厚柳。根metaclass是通過繼承根類產(chǎn)生的氧枣,與根class結(jié)構(gòu)體成員一致,不同的是根metaclass的isa指針指向自身
明白什么是objc_msgSend()
在OC中[objc foo]不會立即執(zhí)行foo方法的代碼别垮,而是在運行時給objc發(fā)送foo的消息便监,這個消息可能會由objc來處理,也可能被轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)給另一個對象碳想,對于不同的消息也可以對應(yīng)一個方法來實現(xiàn)烧董,而這個機制中最重要的方法就是objc_msgSend()
以[objc msgName:param]為例,objc是接收者(receiver)胧奔,msgName:param是選擇器(selector)解藻,而param就是消息(message),message會被編譯器轉(zhuǎn)為標(biāo)準(zhǔn)的C函數(shù):void objc_msgSend(id self, SEL op, ...),而[objc msgName:param]會被轉(zhuǎn)換成:
id returnValue = objc_msgSend(objc, @selector(msgName:), param);
在消息傳遞過程中葡盗,會通過objc的isa指針找到對應(yīng)的類螟左,然后在objc_method_list中查找@selector(msgName:),找不到會按照同樣的方式在繼承樹往上去查找,都找不到的話會拋出異常unrecognized selector send to instance ...觅够,就會發(fā)生消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)胶背。
有人可能會問,如果每次消息傳遞都這樣去遍歷喘先,那效率豈不是太低了嗎钳吟?別擔(dān)心,OC早就考慮到這點了窘拯,注意到結(jié)構(gòu)里面的objc_cache红且,這個的作用就是在消息傳遞查找SEL的時候,一旦查找到對應(yīng)的方法就將它存入緩存中涤姊,下一次進來首先去緩存中去查找暇番,找不到了再往上遍歷,這樣效率就大大提高了思喊。?
消息傳遞過程發(fā)生了什么--message forward
一個類通過已經(jīng)被編譯過的實行方法來確定是否會對某個消息發(fā)出響應(yīng)壁酬,但是如果發(fā)送了一個不能識別的消息給一個類,在編譯時是無法發(fā)現(xiàn)的(通過調(diào)用performSelector:方法),因為所以的方法都能在編譯時動態(tài)添加到方法列表中舆乔,當(dāng)接收者無法識別某個消息時岳服,開發(fā)者可以通過消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)(message forward)機制處理未能識別的message
上面提到的,當(dāng)消息傳遞過程中找不到對應(yīng)的方法時希俩,會拋出unrecognzed selector send to instace ...的錯誤吊宋,即找不到指定的方法,在此之前可以在三個方法中實現(xiàn)補救颜武。
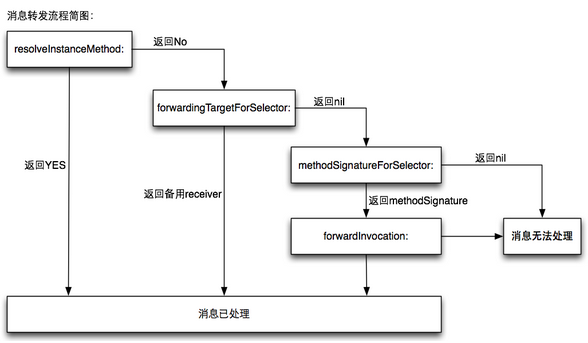
1璃搜、resolveInstanceMethod
將未能識別的消息動態(tài)添加到接收者的類中,resolveInstanceMethod方法返回的是一個BOOL類型的值,用于判斷是否接收這消息盒刚。
先聲明兩個類,Father和Son腺劣,在son中定義個方法:eat绿贞。在Father中創(chuàng)建Son實例因块,然后調(diào)用son的run方法(這個run方法在Son代碼中是未實現(xiàn)的)。
father:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Father : NSObject
@end
#import "Father.h"
#import "Son.h"
@implementation Father
- (void)son {
Son *s = [[Son alloc] init];
[s performSelector:@selector(run)];
}
@end
son:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Son : NSObject
@end
#import "Son.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation Son
void testRun() {
[Son.new eat];
NSLog(@"son is runing");
}
- (void)eat {
NSLog(@"son is eating");
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
//判斷方法是否是run
if ([NSStringFromSelector(sel) isEqualToString:@"run"]) {
class_addMethod([self class], sel, (IMP)testRun, "v@:@");
return YES;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}
@end
打印輸出:
2016-06-27 16:51:49.150 RuntimeDemo[2074:304851] son is eating
2016-06-27 16:51:51.313 RuntimeDemo[2074:304851] son is runing
@selector(run)被動態(tài)添加到了Son的類方法列表中籍铁。
2涡上、forwardindTargetWithSelctor:(SEL)aSelector
當(dāng)resloveInstanceMethod:返回NO之后,會進入forwardindTargetWithSelctor:方法拒名。在這個方法中吩愧,返回的對象就是message的接收者,然后會回到resloveInstanceMethod方法增显,從新開始消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)過程雁佳,如果返回nil則會進入下一個方法中去判斷是否響應(yīng)這個消息。
我們講上面的代碼修改了下變成了這樣
father:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Father : NSObject
@end
#import "Father.h"
#import "Son.h"
@implementation Father
- (void)son {
Son *s = [[Son alloc] init];
[s performSelector:@selector(run)];
}
static void fatherRun() {
NSLog(@"father is runing");
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
if (sel == @selector(run)) {
class_addMethod([self class], sel, (IMP)fatherRun, "v@:@");
return NO;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}
@end
son:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Son : NSObject
@end
#import "Son.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation Son
- (void)eat {
NSLog(@"son is eating");
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
return NO;
}
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
[self eat];
return [Father new];
}
@end
打油啤:
2016-06-27 21:32:21.273 RuntimeDemo[3128:717793] son is eating
2016-06-27 21:32:21.276 RuntimeDemo[3128:717793] father is runing
這就是runtime的神奇之處糖权,消息的接收者由“本應(yīng)該是”的Son轉(zhuǎn)變?yōu)榱?code>Father。
3炸站、forwardingInvocation:anInvocation
當(dāng)resolveInstanceWithSelector:返回NO,forwardingTargetWithSelector:返回nil的時候星澳,就會進入到下一個環(huán)節(jié),使用NSInvocation來實現(xiàn)消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)旱易。
在此之前禁偎,需要調(diào)用methodSignatureForSelector:返回選擇器
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if ([NSStringFromSelector(aSelector) isEqualToString:@"run"]) {
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:"];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
修改上面的代碼為:
father:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Father : NSObject
@end
#import "Father.h"
#import "Son.h"
@implementation Father
- (void)son {
Son *s = [[Son alloc] init];
[s performSelector:@selector(run)];
}
- (void)run {
NSLog(@"father is running");
}
@end
son:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface Son : NSObject
@end
#import "Son.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation Son
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
return NO;
}
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
return nil;
}
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if ([NSStringFromSelector(aSelector) isEqualToString:@"run"]) {
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:"];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation {
Father *f = [[Father alloc] init];
//改變selector
[anInvocation setSelector:@selector(run)];
//在這里指定消息接收者,如果不指定的話還是會拋出找不到方法的異常
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:f];
}
@end
打臃Щ怠:
2016-06-27 22:26:51.604 RuntimeDemo[3605:852405] father is running
我們已經(jīng)成功的將消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)給了Father實例如暖。以上就是消息轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)的流程和具體實踐。
使用objc_associate()為category動態(tài)添加實例變量
眾所周知忌堂,在category中是不允許添加額外的屬性的装处,使用objc_setAssociate()能夠?qū)⒁粋€變量通過指定的key值講實例與實例變量綁定在一起,在讀取的時候值調(diào)用objc_getAssociate(),在指定的實例中通過key將變量取出妄迁,可以簡單理解成字典一樣存取
這兩個方法長這樣:
//setter寝蹈,就像字典中的 setValue:ForKey:
void objc_setAssociatedOject(id object, void *key, id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy)
//getter,就像字典中的 objectForKey
id objc_getAssociatedObject(id object, void *key)
//remove登淘,就像字典中的 removeAllObject
void objc_removeAssocaitedObjected(id object)
在setter方法中箫老,objc_AssociateionPolicy類型相當(dāng)于屬性的strong,assign黔州,copy等耍鬓,它具有以下幾個值:
typedef OBJC_ENUM(uintptr_t, objc_AssociationPolicy) {
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN = 0, //assing
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC = 1, //nonatomic, retain
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC = 3, //nonatomic, copy
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN = 01401, //retain
OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY = 01403 //copy
};
上面說到的,使用這個機制流妻,就像字典一樣設(shè)置牲蜀、讀取key-value,但是它與字典最重要的不同在于:
Though the key is treated purely as an opaque pointer.whereas with a dictionary,keys are regarded equal if they return YES for isEqual:,the key for associated objects must be the exact same point for them to match.For this reason,it is common to use static global variables for the keys.
盡管key被認為是一個不透明的指針绅这,在字典中涣达,只有isEqual:返回的結(jié)果是YES,那么就認為這個兩個key是相等的,但是在associatedObject方法中证薇,key值必須是嚴格相等的度苔,所以通常會使用靜態(tài)的全局變量表示。
在SDWebImage的對UIImageView的分類--UIImageView + WebCache中的獲取當(dāng)前圖片的URL方法:
- (NSURL *)sd_imageURL {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &imageURLKey);
}
而賦值方法是在下載圖片的方法中:
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &imageURLKey, url, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
除此之外還有設(shè)置indicatorStyle的方法:
static char TAG_ACTIVITY_STYLE; //key
/*
對key的處理也可以設(shè)置為具體的值:
static void *TEST_KEY = "TEST_KEY";
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, TEST_KEY, value, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN)
objc_getAssociatedObject(self, TEST_KEY);
*/
.h
- (void)setIndicatorStyle:(UIActivityIndicatorViewStyle)style;
.m
- (void)setIndicatorStyle:(UIActivityIndicatorViewStyle)style{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, &TAG_ACTIVITY_STYLE, [NSNumber numberWithInt:style], OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN);
}
- (int)getIndicatorStyle{
return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, &TAG_ACTIVITY_STYLE) intValue];
}
SEL,Method,Message,IMP
在進入下一個環(huán)節(jié)Method Swizzling之前浑度,需要有一些理論準(zhǔn)備寇窑,否則可能會暈暈的,這些概念在實戰(zhàn)環(huán)節(jié)也會用到箩张,那么甩骏,開始吧。
Selector
a Selector is the name of a method.
Selector是一個方法的名稱先慷,例如咱們都非常熟悉的alloc, init, release, dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:, setObject:forKey:在開發(fā)過程中饮笛,指定按鈕的點擊事件時常用到的@selector(doSomething:),就是指定了方法名。
message:
a message is a selector and the arguments you are sending with it.
message就是包含有參數(shù)的Selector熟掂,例如[dictionary setObject:obj forKey:key],缎浇;這里的Selector就是setObject:forKey:
method
a method is a combination of a selector and an implementation (and accompanying metadata).
method是Selector和implementation的結(jié)合
還有:
IMP
IMP就是implementation的縮寫。
the actual executable code of a method. Its type at runtime is an IMP, and it's really just a function pointer.
好吧赴肚,這個概念應(yīng)該比較不會混淆素跺,不過需要注意的是,implementation在runtime中就是一個函數(shù)指針
一個類維護一個運行時可接收的消息分發(fā)表誉券;分發(fā)表中的每個入口是一個方法(Method)指厌,其中key是一個特定名稱,即選擇器(SEL)踊跟,其對應(yīng)一個實現(xiàn)(IMP)踩验,即指向底層C函數(shù)的指針鸥诽。
method swizzling
method swizzling可以說是runtime的黑魔法,它可以交換兩個方法的IMP箕憾,攔截系統(tǒng)的方法牡借,添加更多的功能,例如:調(diào)用方法后自動log輸出袭异,再也不用傻傻的一次次去NSLog了钠龙,關(guān)于method swizzling更多的內(nèi)容,可以看看我之前寫的黑魔法 - Method Swizzling
實戰(zhàn)
動態(tài)創(chuàng)建類御铃,對象碴里,方法,實例變量
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <objc/runtime.h>
#import <objc/message.h>
static void speak(id self, SEL _cmd, id some) {
NSLog(@"some of %@ %@ years old named %@ say: %@",
[self class],
[self valueForKey:@"age"],
object_getIvar(self, class_getInstanceVariable([self class], "name")) ,some);
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
//創(chuàng)建一個 Person 的類
Class Person = objc_allocateClassPair([NSObject class], "Person", 0);
//添加一個 name 的實例變量上真,現(xiàn)在是為賦值狀態(tài)咬腋,僅僅是在objc_class的ivars里面添加了ivar
class_addIvar(Person, "name", sizeof(NSString *), log2(sizeof(NSString *)), @encode(NSString *));
class_addIvar(Person, "age", sizeof(int), sizeof(int), @encode(int));
//注冊一個speak的方法
SEL sayHello = sel_registerName("sayHello:");
//往 Person 的 methodLists里面添加方法
class_addMethod(Person, sayHello, (IMP)speak, "v@:@");
//在創(chuàng)建實例之前需要先注冊類
objc_registerClassPair(Person);
//初始化 Person 實例
id person = [[Person alloc] init];
//為name,age賦值
[person setValue:@"xiaoming" forKey:@"name"];
Ivar age = class_getInstanceVariable(Person, "age");
object_setIvar(person, age, @25);
//發(fā)送消息
//objc_msgSend(person, sayHello, @"大家好!");
((void(*)(id, SEL,id))objc_msgSend)(person, sayHello, @"Hello World!");
}
return 0;
}
獲取全部屬性睡互,實例根竿,方法
- (NSDictionary *)allIvars {
NSLog(@"=======ivars=========");
unsigned int count = 0;
NSMutableDictionary *allIvar = @{}.mutableCopy;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
if (count == 0) { return allIvar; }
for (NSUInteger i = 0; i < count; i++) {
char const *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivars[i]);
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarName];
id ivar = [self valueForKey:name];
if (ivar) {
allIvar[name] = ivar;
}else {
allIvar[name] = @"value為nil";
}
}
//數(shù)組指針需要用free去釋放
free(ivars);
NSLog(@"=======ivars=========");
return allIvar;
}
- (NSDictionary *)allProperty {
NSLog(@"=======properties=========");
unsigned int count = 0;
NSMutableDictionary *allProperty = @{}.mutableCopy;
objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList([self class], &count);
if (count == 0) { return allProperty; }
for (NSUInteger i = 0; i < count; i++) {
char const *propertyName = property_getName(properties[i]);
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:propertyName];
id property = [self valueForKey:name];
if (property) {
allProperty[name] = property;
}else {
allProperty[name] = @"property為nil";
}
}
//數(shù)組指針需要用free去釋放
free(properties);
NSLog(@"=======properties=========");
return allProperty;
}
- (NSDictionary *)allMethod {
NSLog(@"=======methods=========");
unsigned int count = 0;
NSMutableDictionary *allMethod = @{}.mutableCopy;
Method *methods = class_copyMethodList([self class], &count);
if (count == 0) { return allMethod; }
for (NSUInteger i = 0; i < count; i++) {
SEL sel = method_getName(methods[i]);
char const *mehtodName = sel_getName(sel);
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:mehtodName];
int arguments = method_getNumberOfArguments(methods[i]);
allMethod[name] = @(arguments-2);
}
//數(shù)組指針需要用free去釋放
free(methods);
NSLog(@"=======methods=========");
return allMethod;
}
統(tǒng)一歸檔、解檔
通常情況下湃缎,使用NSCoding歸檔犀填,解檔的時候是一個變量一個屬性進行的蠢壹,假設(shè)一個類中有1000個變量呢嗓违,那不是要瘋了嗎?好在咱們有runtime這個神器图贸,如果能夠直接取出全部的實例變量列表蹂季,那不就是一個for循環(huán)的事情了嗎?
//解檔
- (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) {
char const *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivars[i]);
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarName];
id value = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:name];
[self setValue:value forKey:name];
}
free(ivars);
return self;
}
//歸檔
- (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder {
unsigned int count = 0;
Ivar *ivars = class_copyIvarList([self class], &count);
for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) {
char const *ivarName = ivar_getName(ivars[i]);
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivarName];
id value = [self valueForKey:name];
[aCoder encodeObject:value forKey:name];
}
free(ivars);
}