@[TOC](多線程與高并發(fā))
# 認識并發(fā)與并行
并發(fā)是針對一個CPU來講忠烛,“同一時間”執(zhí)行多個任務--實質上是劃分時間片,由于時間很短給人的感覺是是同時執(zhí)行的冰沙;
并行是針對多個CPU來講的,同時執(zhí)行多個任務(一個CPU執(zhí)行一個),這是真正意義上的同時執(zhí)行叼屠;
## 入門程序分析(打印---HelloWorld)
```java
class Car{
? ? public void drive(){
? ? ? ? System.out.println("我會跑");
? ? }
}
public class HuiXinThread {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ? Car car=null;
? ? ? ? System.out.println("HelloWorld");//主線程---main()
? ? ? ? car.drive();//異常處理的線程---
? ? ? ? new Car().drive();//運行完畢,new Car()匿名對象會被回收--垃圾收集器
? ? }
}
```
所以在我們初學java時绞铃,并非只有一個線程镜雨,其實是多線程的包括? 主線程、處理異常的線程儿捧,以及垃圾收集器線程等等冷离;
### 線程之間是如何搶占CPU資源的?
先來看一個案例----
當我們打開一個程序前纯命,其實就是存放在電腦中的代碼(靜態(tài)的)西剥,打開之后,這個程序才算開啟亿汞,(為他分配空間以及CPU資源)瞭空,然后在這個程序中開啟不同的功能--即開啟了多個線程,然后CPU再次為這些線程服務疗我,如果線程過多咆畏,CPU不夠用,那就會使得一個CPU要執(zhí)行多個線程---形成了并發(fā)(采用時間片機制)吴裤,同時可以為線程設置優(yōu)先級來提高相應線程被先執(zhí)行的概率(并不是優(yōu)先級低就一定會被后執(zhí)行)
### 自定義線程的執(zhí)行
線程的創(chuàng)建方式---
第一種---繼承Thread類
```java
class Car extends? Thread{
? ? @Override
? ? public void run(){
? ? ? ? for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
? ? ? ? System.out.println("我會跑");}
? ? }
}
public class HuiXinThread {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ? //主線程---main()
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println("HelloWorld"+i);
? ? ? ? }
? ? new Car().run();
? ? }
}
```
這一種并不是多線程旧找,因為該方式只是把run()當成一個普通方法來執(zhí)行的;麦牺,所以運行結果是 先執(zhí)行main--主線程钮蛛,然后執(zhí)行run()鞭缭,此時run也是屬于主線程里面的;

```java
class Car extends? Thread{
? ? @Override
? ? public void run(){
? ? ? ? for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
? ? ? ? System.out.println("我會跑");}
? ? }
}
public class HuiXinThread {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ? //主線程---main()
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println("HelloWorld"+i);
? ? ? ? }
? ? new Car().start();
? ? }
}
```
start()是父類的方法魏颓,但是與逆行結果依然跟上面一樣---
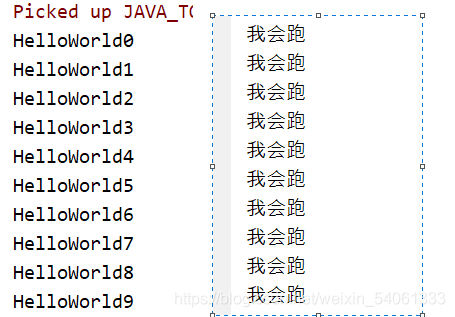原因是我們在主線程(for循環(huán))執(zhí)行時并沒有子線程參與進來岭辣,要想實現(xiàn)并發(fā)效果需要調整一下start()方法的位置--
```java
class Car extends? Thread{
? ? @Override
? ? public void run(){
? ? ? ? for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
? ? ? ? System.out.println("我會跑"+i);}
? ? }
}
public class HuiXinThread {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ? //子線程
? ? ? ? new Car().start();
? ? ? ? //主線程---main()
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println("HelloWorld"+i);
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
}
```

> 運行后發(fā)現(xiàn)---有時候并不一定會出現(xiàn)并發(fā)---當運行量少的時候;
# 為線程設置名字和獲取線程名字
```java
public class Car extends? Thread{
? ? @Override
? ? public void run(){
? ? ? ? for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println(this.getName()+i);}
? ? }
}
public class HuiXinThread {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ? //子線程
? ? ? ? ? ? Car car= new Car();
? ? ? ? ? ? car.setName("小汽車");
? ? ? ? car.start();
? ? ? ? //主線程---main()
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+i);
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
}
```

還可以通過構造器來設置線程名字---
```java
public class Car extends? Thread{
? ? public Car(String name){
? ? ? ? super(name);
? ? }
? ? @Override
? ? public void run(){
? ? ? ? for (int i=0;i<10;i++){
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println(this.getName()+i);}
? ? }
}
public class HuiXinThread {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ? //子線程
? ? ? ? ? ? Car car= new Car("小火車");
? ? ? ? ? ? //car.setName("小汽車");
? ? ? ? car.start();
? ? ? ? //主線程---main()
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+i);
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
}
```

設置線程名的父類構造方法---

# 線程開啟的方式---
## 繼承Thread類--
演示代碼如上甸饱,不在贅述----注意點為? 開啟線程是start()方法沦童,而run()方法還是當作一個普通方法來處理的;
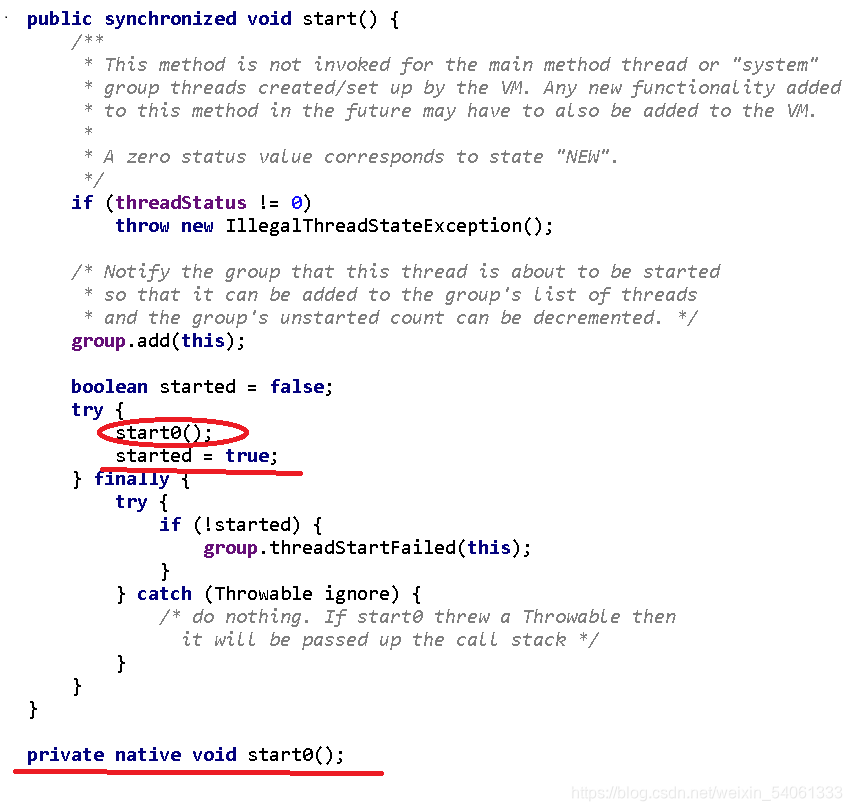
start()源碼---
> 此方法不為主方法線程或“系統(tǒng)”調用叹话。?
> 虛擬機創(chuàng)建/設置的組線程偷遗。 添加的新功能?
> 到這個方法以后可能還需要添加到VM中。
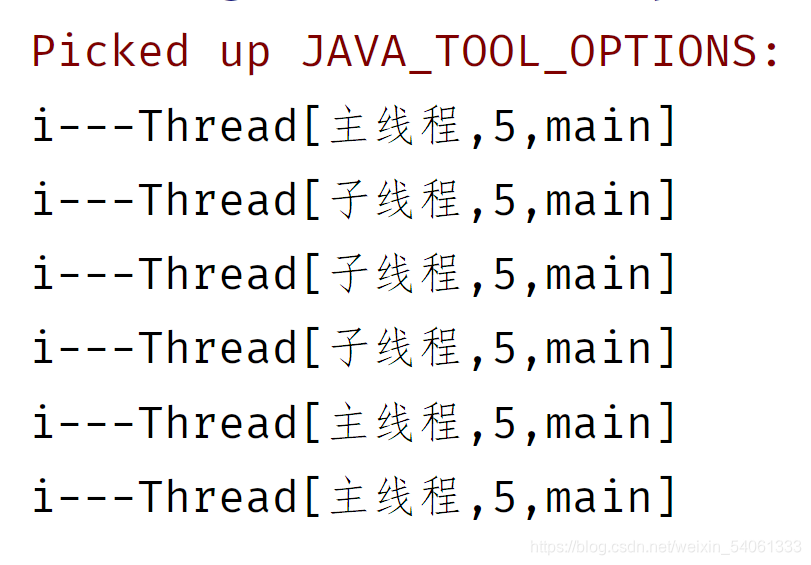
## 實現(xiàn)Runable接口
```java
class BuyBook implements Runnable{
? ? @Override
? ? public void run() {
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println("i---"+Thread.currentThread());
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
}
public class Test {
? ? public static void main(String[] args)? {
? ? ? ? BuyBook bb= new BuyBook();
? ? ? ? bb.run();
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println("i---"+Thread.currentThread());
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
}
```
> Runnable接口中只有一個run方法,

并沒有發(fā)現(xiàn)start方法,需要怎么做呢?
start()方法在Thread類中,所以要先在創(chuàng)建一個Thread的對象
```java
class BuyBook implements Runnable{
? ? @Override
? ? public void run() {
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println("i---"+Thread.currentThread());
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
}
public class Test {
? ? public static void main(String[] args)? {
? ? ? ? Thread.currentThread().setName("主線程");
? ? ? ? BuyBook bb= new BuyBook();
? ? ? ? Thread thread= new Thread(bb);
? ? ? ? thread.setName("子線程");
? ? ? ? thread.start();
? ? ? ? for (int i = 0; i <3 ; i++) {
? ? ? ? ? ? System.out.println("i---"+Thread.currentThread());
? ? ? ? }
? ? }
}
```
> public Thread(Runnable target) {//構造器--傳入的是Runnable對象
? ? ? ? this(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
? ? }
當處理量少的時候得到的結果像是順序執(zhí)行的,多運行幾次就可以了;