本文分析使用的MyBatis 源代碼版本為3.4.1
在上一篇文章:MyBatis3教程 - MyBatis插件(Plugins)開發(fā) 中已經(jīng)介紹了如何去開發(fā)一個MyBatis 插件碗旅,本文將結(jié)合MyBatis 源碼來揭秘MyBatis Plugins內(nèi)部實(shí)現(xiàn)原理。
Mybatis3 插件采用責(zé)任鏈模式销部,通過動態(tài)代理組織多個攔截器(插件)眠饮,通過這些攔截器可以改變Mybatis的默認(rèn)行為(諸如SQL重寫之類的)奥帘。
先來看看上一篇文章中實(shí)現(xiàn)的插件,代碼如下:
package com.bytebeats.mybatis3.interceptor;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.statement.StatementHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.*;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* ${DESCRIPTION}
*
* @author Ricky Fung
* @date 2017-02-17 11:52
*/
@Intercepts({ @Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "prepare", args = { Connection.class, Integer.class}) })
public class SQLStatsInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
logger.info("mybatis intercept sql:{}", sql);
return invocation.proceed();
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
String dialect = properties.getProperty("dialect");
logger.info("mybatis intercept dialect:{}", dialect);
}
}
實(shí)現(xiàn)原理分析
Mybatis支持對Executor仪召、StatementHandler寨蹋、PameterHandler和ResultSetHandler 接口進(jìn)行攔截松蒜,也就是說會對這4種對象進(jìn)行代理。
下面以Executor接口為例已旧,org.apache.ibatis.executor.SimpleExecutor 在執(zhí)行doUpdate秸苗、doQuery、doQueryCursor方法時會執(zhí)行如下代碼:
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null);
順藤摸瓜运褪,我們來看看org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration 類惊楼,其代碼如下:
public class Configuration {
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
/**對ParameterHandler 進(jìn)行攔截**/
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
/**對ResultSetHandler 進(jìn)行攔截**/
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
/**對StatementHandler 進(jìn)行攔截**/
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
/**對Executor 進(jìn)行攔截**/
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
return newExecutor(transaction, defaultExecutorType);
}
/**對Executor 進(jìn)行攔截**/
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
我們重點(diǎn)關(guān)注這行代碼:
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
上面代碼功能是:對statementHandler 插入所有的Interceptor以便進(jìn)行攔截,InterceptorChain里保存了所有的攔截器秸讹,它在Configuration 對象被構(gòu)造出來的時候創(chuàng)建檀咙。
org.apache.ibatis.plugin.InterceptorChain 源代碼如下:
public class InterceptorChain {
private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>();
public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
target = interceptor.plugin(target);
}
return target;
}
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
interceptors.add(interceptor);
}
public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() {
return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors);
}
}
org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Interceptor 類的代碼如下:
public interface Interceptor {
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
Object plugin(Object target);
void setProperties(Properties properties);
}
org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Invocation 代碼如下:
public class Invocation {
private Object target;
private Method method;
private Object[] args;
public Invocation(Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
this.target = target;
this.method = method;
this.args = args;
}
public Object getTarget() {
return target;
}
public Method getMethod() {
return method;
}
public Object[] getArgs() {
return args;
}
public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
return method.invoke(target, args);
}
}
org.apache.ibatis.plugin.Plugin 源代碼如下:
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
private Object target;
private Interceptor interceptor;
private Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
}
責(zé)任鏈模式
責(zé)任鏈模式(Chain Of Responsibility Pattern )在 Wiki 上定義如下:
責(zé)任鏈模式在面向?qū)ο蟪淌皆O(shè)計里是一種軟件設(shè)計模式,它包含了一些命令對象和一系列的處理對象璃诀。每一個處理對象決定它能處理哪些命令對象弧可,它也知道如何將它不能處理的命令對象傳遞給該鏈中的下一個處理對象。該模式還描述了往該處理鏈的末尾添加新的處理對象的方法劣欢。
23種設(shè)計模式中非常經(jīng)典的一個設(shè)計模式侣诺。
責(zé)任鏈模式應(yīng)用
1、Servlet FilterChain
package com.bytebeats.mario.web;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
public class CharacterEncodingFilter implements Filter {
public void init(FilterConfig config) throws ServletException {
}
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
public void destroy() {
}
}
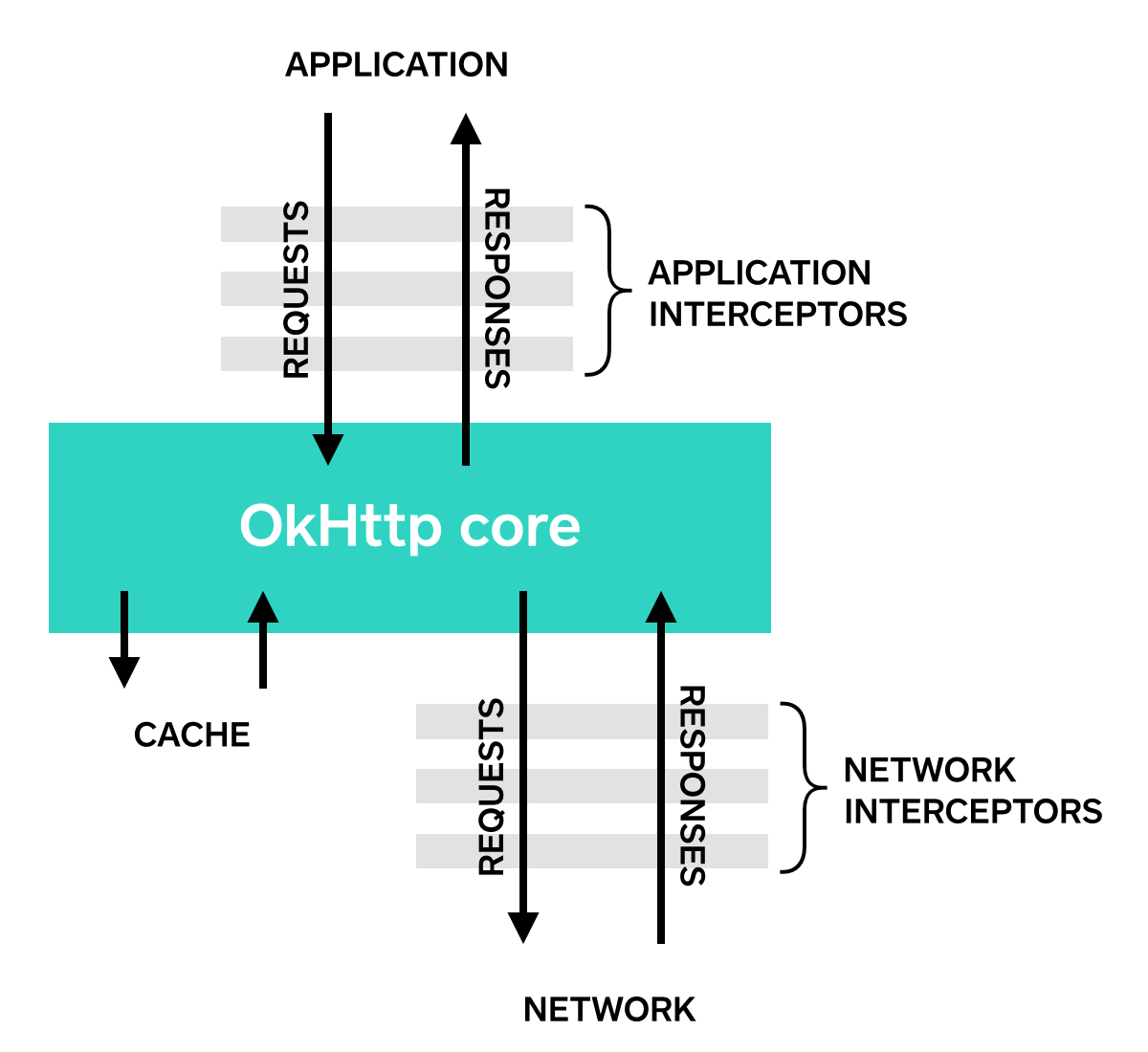
2氧秘、OkHttp Interceptors**
OkHttp Interceptors:https://github.com/square/okhttp/wiki/Interceptors